Conventional optical microscopy is limited to a sample magnification of approximately 1000x, due to the wavelength range of visible light (400—700nm). Two distinct points on a sample can be optically resolved using a standard microscope if they are no closer than ~0.2 micrometers (μm) to one another.
Although groundbreaking in its time, the compound microscope has quickly fallen behind alternative tools capable of performing high-precision materials characterization or insights into molecular activities on the nanoscale.
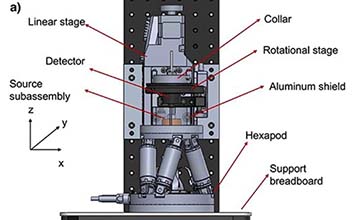
Numerous techniques have been developed to overcome the limited resolving power of conventional microscopes. Super-resolution optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and much more have emerged as suitable candidates for surface metrology. All of these methods require some kind of motion – in the case of SEM, an electronic beam can be deflected without using mechanical components. In the case of AFM and super resolution optical microscopy, precision mechanisms are required to move the probe or sample.
Outlining Piezo-Based Nano-Positioning Equipment
Often piezo mechanics are used because of their virtually unlimited resolution and fast response. Piezo nano-positioning stages are used to adjust, align or scan the position of samples with sub-atomic resolution, providing the most accurate positioning currently possible for micro- and nanoscopic imaging. Piezo mechanisms can also rapidly respond to a control signal in less than one millisecond. This has proven instrumental for fast-focussing and 3D imaging applications.
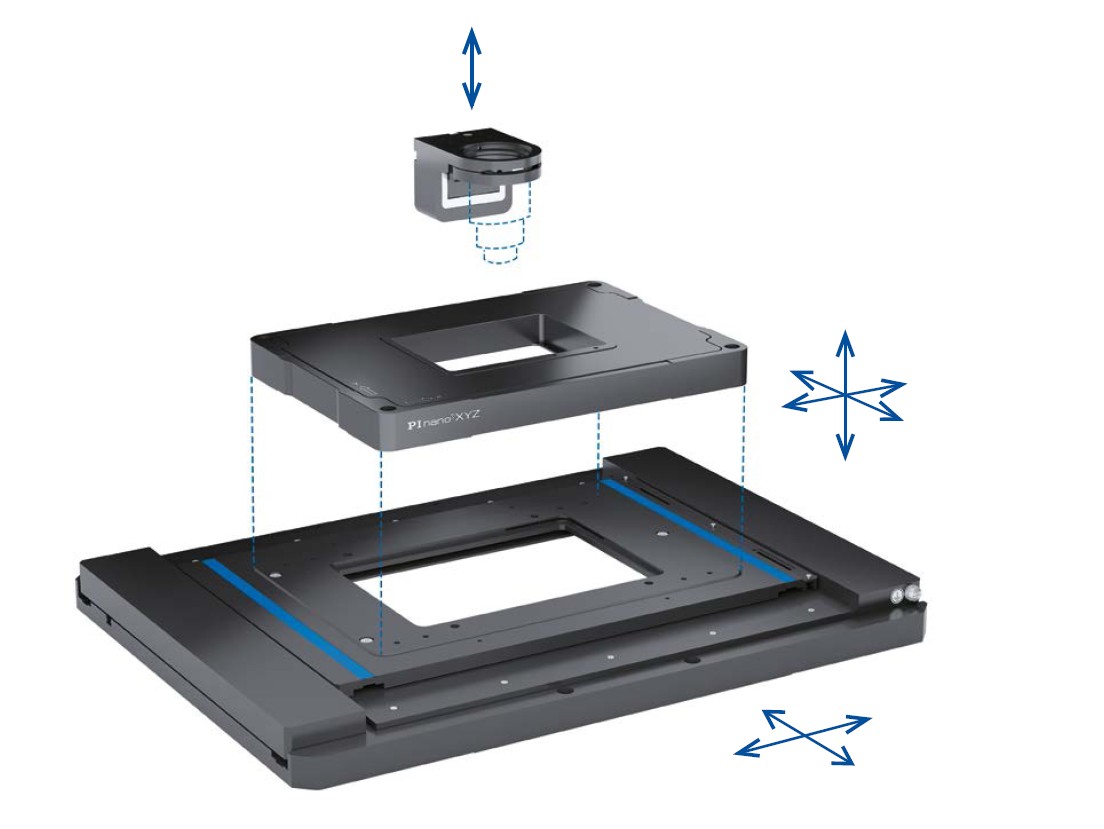
Piezo-based positioning equipment can be easily integrated into research and OEM equipment for reliable testing at industrial-scale speeds. Most nanopositioning stages are flexure guided (wear-, friction- and maintenance free) and driven by piezo transducers, which are ceramic actuators capable of converting an electric charge into rapid linear motion and force with practically unlimited resolution. Even tiny changes in operating voltage are converted into controlled movements which enable extremely fine positional adjustments down to the sub-nanometer range. While piezo-flexure nano-positioners provide a motion range of typically 100µm to 1mm, different types of piezo motors are available for long travel microscope stages. Here the piezo motors provide high stability due to their self-locking nature, once a position has been reached.
Alongside their outstanding precision, piezo-based positioning equipment is also extremely reliable and can also be engineered into very compact, low-profile motion systems.
Nano-Positioning Equipment from PI
PI offers a range of positioning equipment suitable for sub-nanometre resolution microscopy and interferometry. Our XY and XYZ piezo flexure scanners are designed to mount on either manual or motorized microscope stages with easy housing or slides and additional inserts. PI piezo Z-scanners generally achieve as much as 10x the precision and focussing speed than alternative motorized positioning equipment. These include:
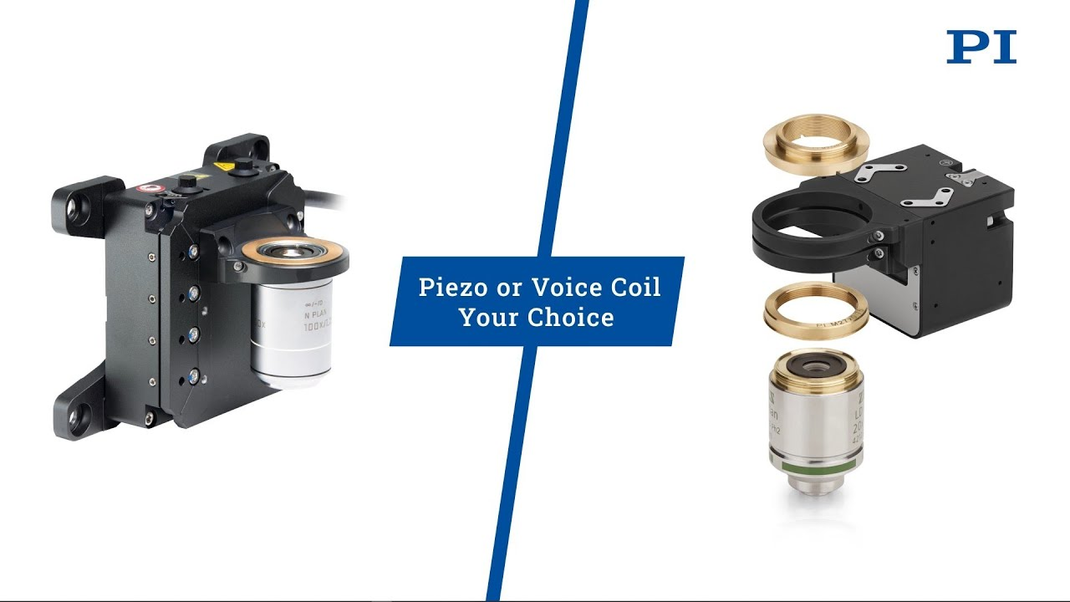
- P-736 Piezo-Z Sample Scanner: With a range of vertical motion up to 220μm and a resolution of a single nanometer, this low-profile Z-scanner is available for both microscopic slides and multiple well-plates for microbiology and life sciences studies.
- P-725 PIFOC Objective Scanner: With a millisecond response time and 400µm of vertical travel the Z-scanner is ideal for high throughput microscopy and biotechnology screening and testing applications.
If you would like to learn more about our precision positioning equipment for microscopy applications, read our previous blog post Advanced in Precision Motorized Positioning Systems: Selection Criteria. Otherwise, to contact us directly if you have any questions.
Blog Categories
- Aero-Space
- Air Bearing Stages, Components, Systems
- Astronomy
- Automation, Nano-Automation
- Beamline Instrumentation
- Bio-Medical
- Hexapods
- Imaging & Microscopy
- Laser Machining, Processing
- Linear Actuators
- Linear Motor, Positioning System
- Metrology
- Microscopy
- Motorized Precision Positioners
- Multi-Axis Motion
- Nanopositioning
- Photonics
- Piezo Actuators, Motors
- Piezo Mechanics
- Piezo Transducers / Sensors
- Precision Machining
- Semicon
- Software Tools
- UHV Positioning Stage
- Voice Coil Linear Actuator
- X-Ray Spectroscopy