We’re at the dawning of the age of space-based free space optical communication. Numerous tech enterprises are actively engaged in the deployment of extensive low earth orbit (LEO) space-based communication networks, featuring compact satellites as their primary nodes. These satellites, numbering in the thousands, will be launched into orbit, utilizing laser light for interconnection and efficient global data transmission.
Simultaneously, a comparable method for establishing point-to-point networks is emerging on Earth through the innovative concept of "fiberless photonics." This groundbreaking approach holds the potential to swiftly establish secure connections between various locations, such as linking buildings in densely populated cities or serving as the "last mile" in broader network setups.
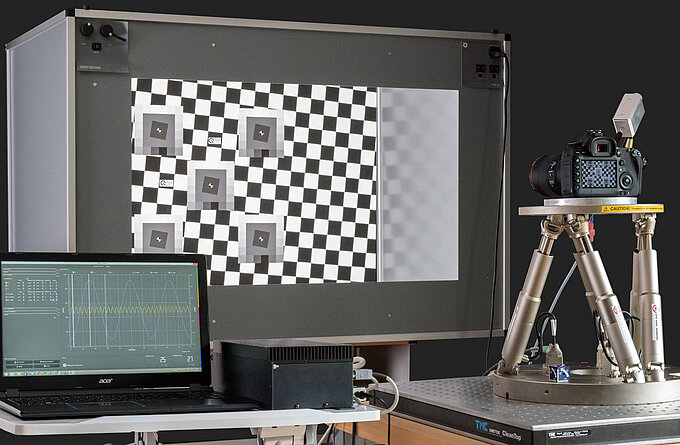
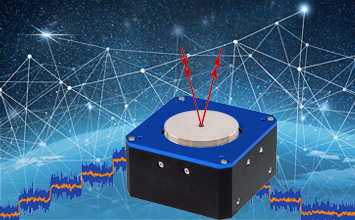
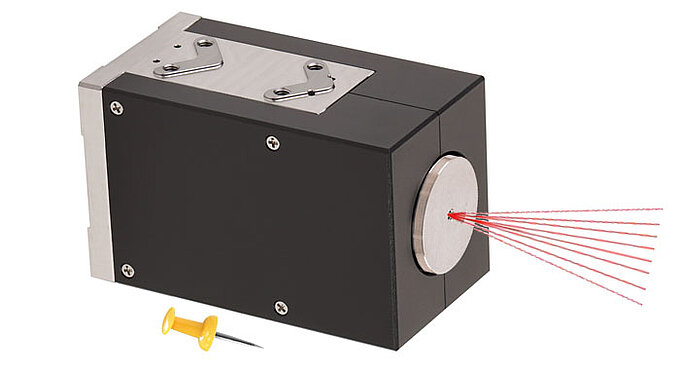
In both free-space communication applications – on earth and in space – fast laser steering mirrors (FSMs) are required to point and stabilize the beam for error-free data transmission.
PI COTS Laser Steering Mirrors Already in Orbit
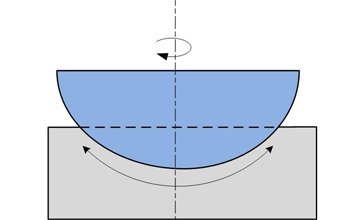
Pioneering LEO network operators have successfully deployed PI FSMs in their communication satellites and have confirmed their unrestricted suitability for use in space. For other operators, PI engineers have developed electromagnetically driven tip/tilt mirror systems (voice coil FSMs) for larger deflections. To manufacture them, PI has invested in a highly automated production line under cleanroom conditions. Also, these voice coil FSMs are already in use in space.
Signal Finding and Optimization Algorithms
PI engineers understand mission-critical 24/7 acquisition and tracking and our hardware designs are informed by it. We recently launched a new first-light finding algorithm for fiber optical alignment applications that is orders of magnitudes faster than conventional search algorithms.