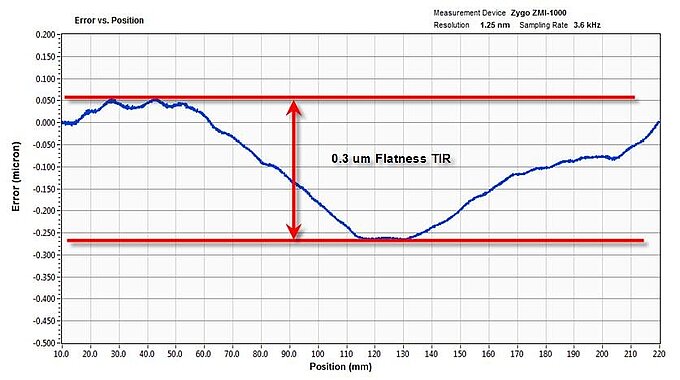
As of April 2023, NASA alone has launched a total of 115 CubeSats. In addition to these tiny satellites, thousands of small satellites have been sent into orbit since 2019, when Starlink started their space-based internet, and with the growing global interest in free space optical communication, some forecasts predict up to 100,000 units might be orbiting Earth by the end of the decade. The various commercial and academic institutions building these satellites are constantly in the process of developing improved test systems that fully validate their hardware before deploying systems for launch.
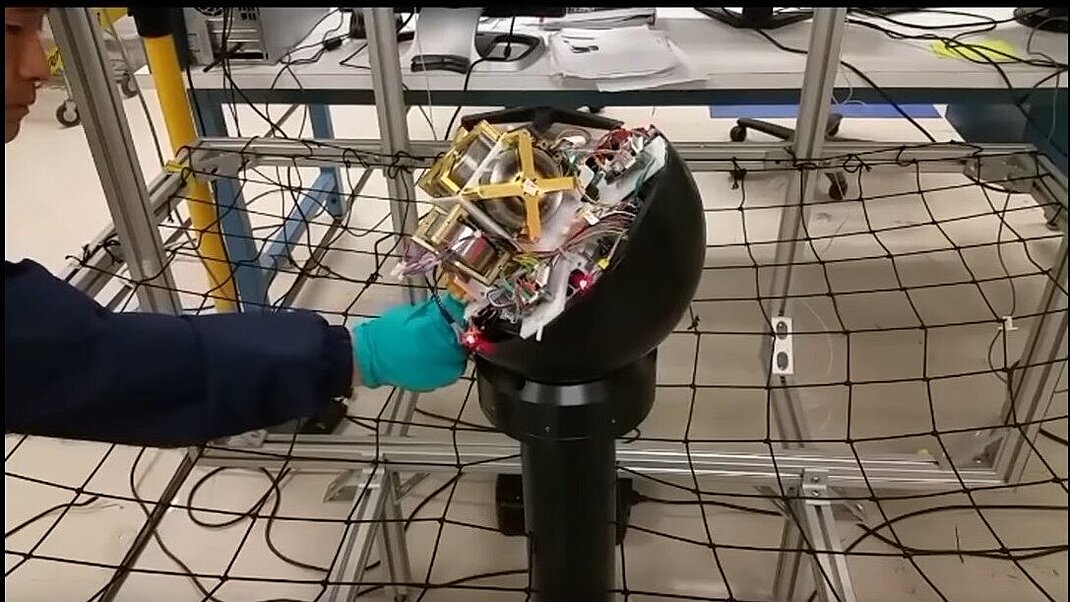
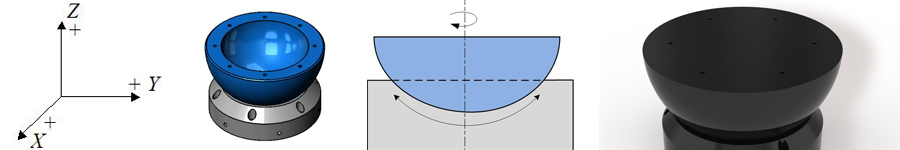
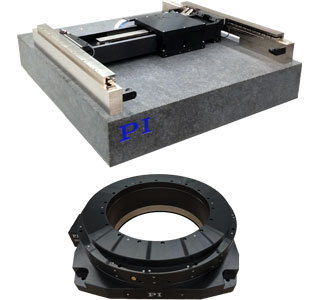
PIglide HB Spherical Air Bearings are commonly used to test the attitude control systems of small satellites. The frictionless nature of the spherical air bearing partially simulates a zero-g environment, allowing the pitch, roll, and yaw control systems of the satellite to work as they would in space, without resorting to traditional drop testing or other cumbersome and expensive test simulations.
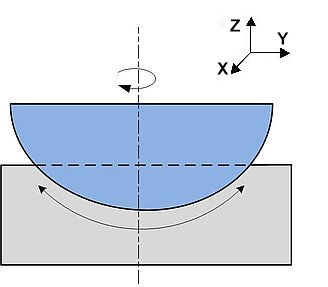
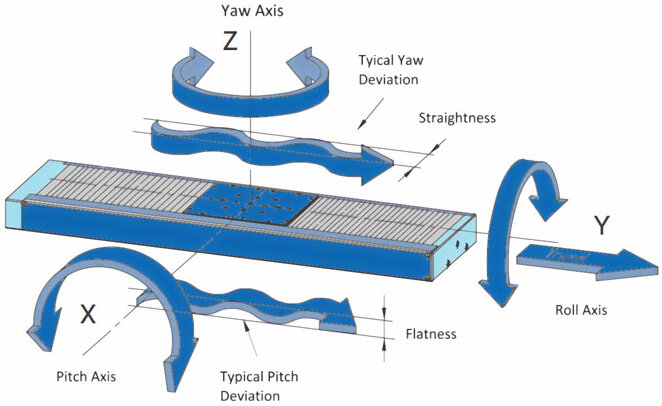
A spherical air bearing provides frictionless motion in three degrees of freedom: unrestrained rotation about the vertical Z axis, and +/-45° tilt motion about the horizontal X and Y axes.
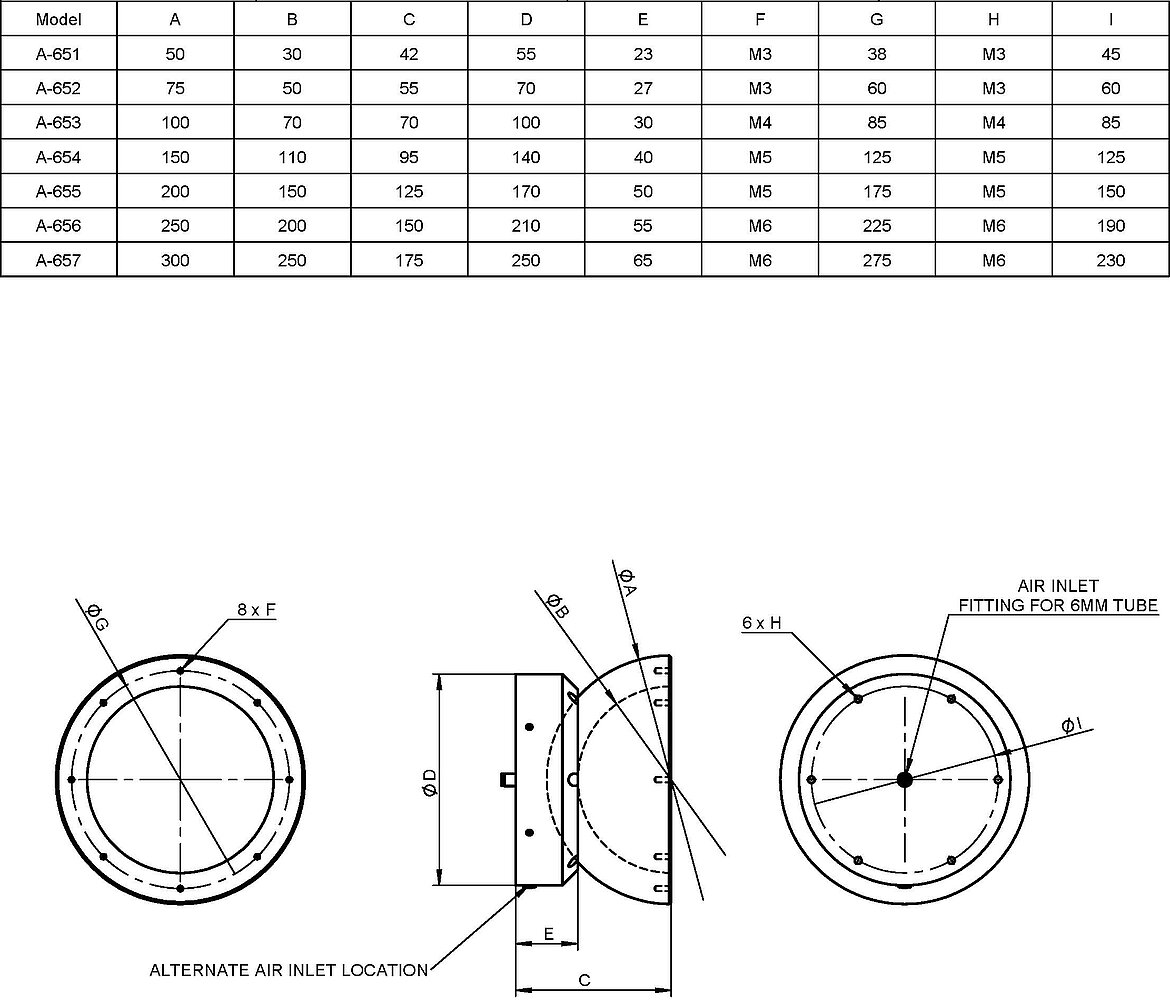
PIglide HB series spherical air bearings range in size from 50mm up to 300mm and can carry payloads from less than 10kg up to 635kg when supplied with compressed air at 80 psi. This wide range of sizes offers a solution for nearly any small satellite, from 1U picosatellites up to half-ton minisatellites.
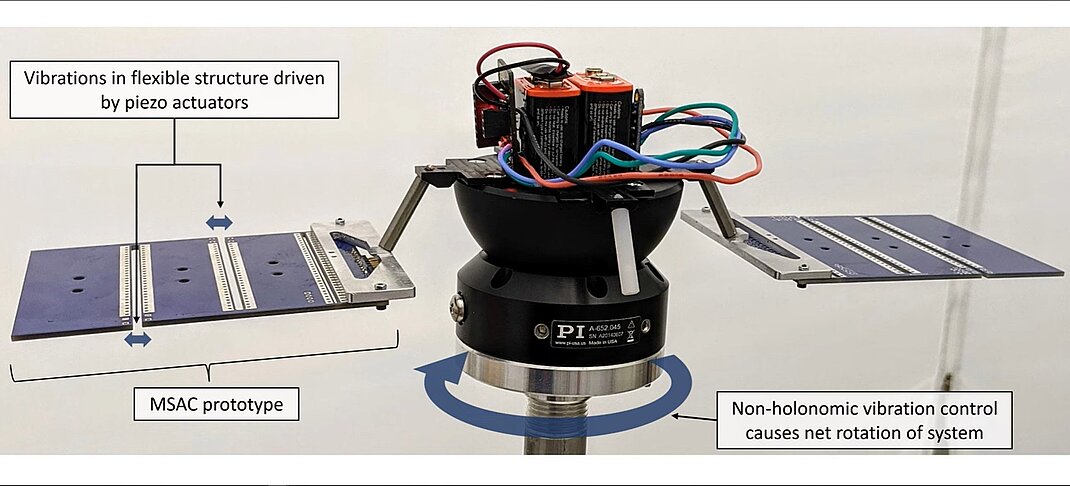
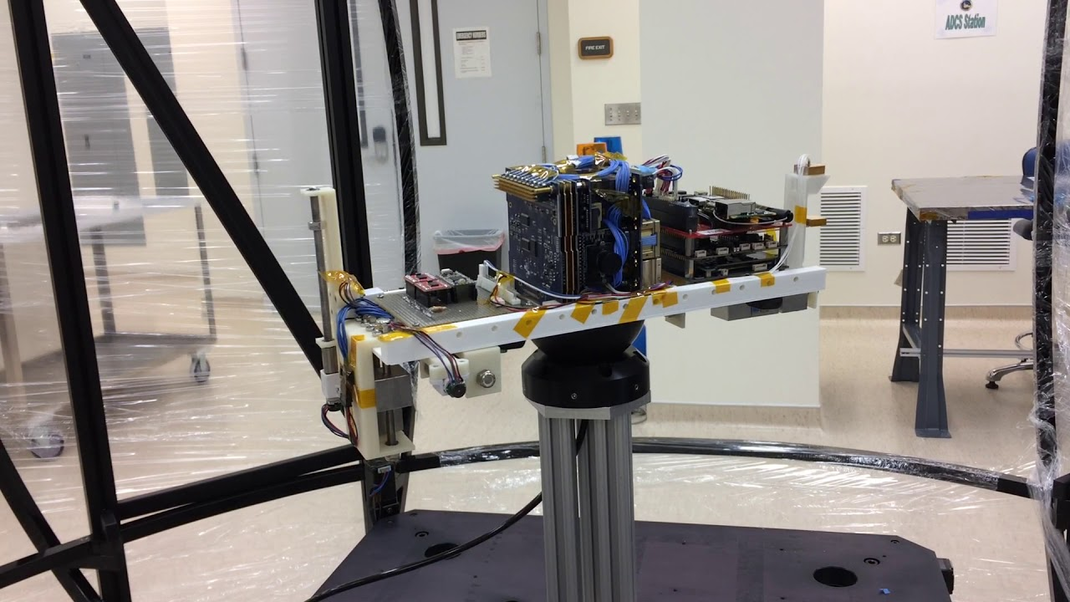
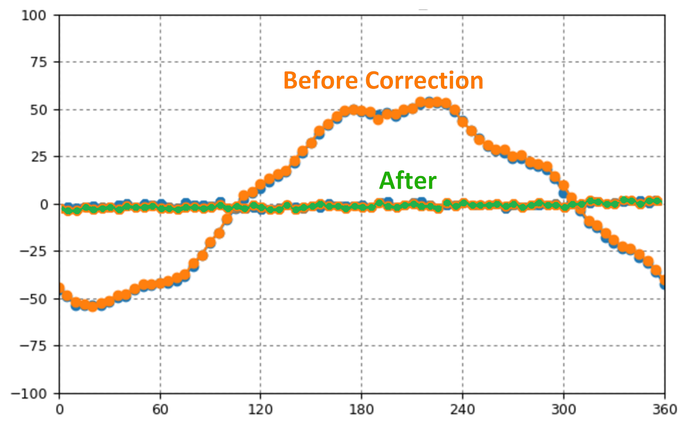
The video shows the Hardware-in-the-Loop results for a high-fidelity distributed piezoelectric actuator-based prototype executing both clockwise and counter-clockwise slews. The MSAC concept currently stands at a Technology Readiness Level of 5.
The moving element of the PIglide HB spherical air bearing is made as lightweight as possible so as to reduce moving mass and moment of inertia. This helps ensure that the test system simulates the actual satellite behavior and characteristics as closely as possible.
The spherical air bearing is often used with a pedestal mount to raise the test platform off the ground and to provide clearance for the satellite under test to rotate and tilt freely.
Can Air Bearings work in a Vacuum?
The paper "Attitude Testing Platform in a Vacuum Environment for a Lean Satellite with an Electric Thruster" by Marcos Hernandez-Herrera et al, discusses the development of a testing platform designed to evaluate attitude control systems (ACS) for small satellites, particularly those utilizing electric propulsion systems (EPS) such as vacuum arc thrusters (VAT) and pulsed plasma thrusters (PPT).
Electric thrusters, like VATs and PPTs, operate by ionizing a propellant material to generate plasma, which is then accelerated to produce thrust. This method offers precise control over small thrust levels, making them suitable for fine-tuning satellite orientation and position.
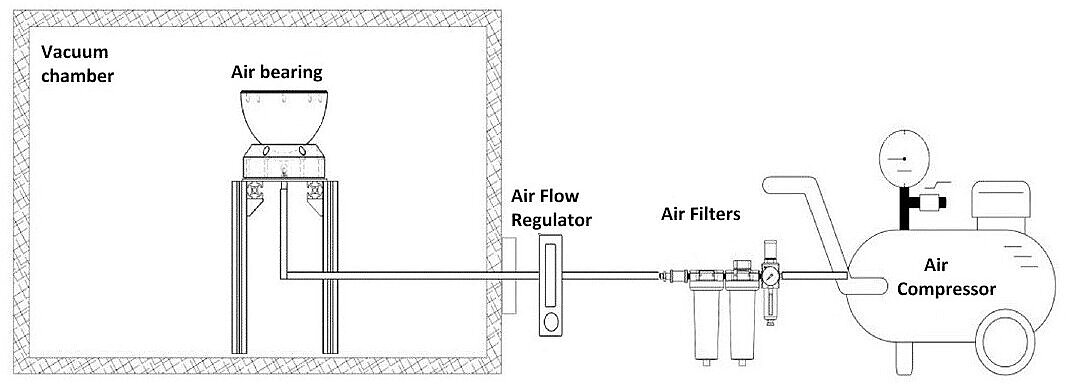
In the context of the research paper, the VAT is used as an actuator on the testing platform to provide controlled rotational motion. The platform, equipped with a spherical air bearing, allows frictionless rotational movement in three degrees of freedom within a vacuum chamber. By igniting the VAT, the researchers induced rotation in the platform, enabling them to measure the angular rate and evaluate the thruster's performance.
The successful operation of the VAT within the vacuum environment demonstrated its capability to produce measurable thrust impulses, validating its application for attitude control in lean satellites. This testing platform provides a valuable tool for assessing and verifying the performance of electric thrusters in conditions that closely simulate the space environment.
Frictionless Motion in more than 3 Degrees of Freedom
For test situations where more than three degrees of freedom are required (i.e. if translation in X or Y is required), the spherical bearing can be mounted on top of a linear air bearing slide, such as the PIglide RB. If motion in both X and Y are required, two PIglide RB slides can be stacked with the PIglide HB spherical air bearing mounted in top. A planar XY puck design can also be used.
More Motion Control Solutions for Aerospace Applications
In addition to the spherical air bearings PI also provides other solutions for space applications, such as 6DOF hexapod positioning systems that can be used in the validation of optical terminals, such as the OTVT at the MIT Lincoln Laboratory and fast steering mirrors for free space optical communication in LEO satellites.

Contact us today at air@pi-usa.us to discuss how we can solve your precision motion challenge.
References
- The Ranging And Nanosatellite Guidance Experiment (RANGE)
- http://www.space-electronics.com/Literature/SAWE_Papers/Spherical_Gas_Bearing_Weightlessness.pdf
- http://ssl.mit.edu/files/website/theses/SM-2014-PrinkeyMeghan.pdf
- http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.330.8750&rep=rep1&type=pdf
- http://faculty.nps.edu/agrawal/docs/spie-agrawal-rasmussen.pdf
- http://www.cubesat.org/
- http://www.floridatoday.com/story/tech/science/space/2015/05/16/nasa-seeks-launchers-smallest-satellites/27392049/
Blog Categories
- Aero-Space
- Air Bearing Stages, Components, Systems
- Astronomy
- Automation, Nano-Automation
- Beamline Instrumentation
- Bio-Medical
- Hexapods
- Imaging & Microscopy
- Laser Machining, Processing
- Linear Actuators
- Linear Motor, Positioning System
- Metrology
- Microscopy
- Motorized Precision Positioners
- Multi-Axis Motion
- Nanopositioning
- Photonics
- Piezo Actuators, Motors
- Piezo Mechanics
- Piezo Transducers / Sensors
- Precision Machining
- Semicon
- Software Tools
- UHV Positioning Stage
- Voice Coil Linear Actuator
- X-Ray Spectroscopy