The choice of feedback sensor is one of the key performance factors of a piezo positioning stage. Below is a comparison between the two most commonly used sensors. When the absolute positioning information plays a critical role in scientific results, researchers prefer capacitive sensors. When cost is most important and / or results are based on relative position, the more economical piezoresistive sensors are just fine. PI provides stages with both options plus a variety of other sensor choices as well, depending on parameters such as sensitivity, stability, dynamics, cost, etc. It is important to understand the application and how the positioning performance affects the results to recommend the sensor best suited to the application.
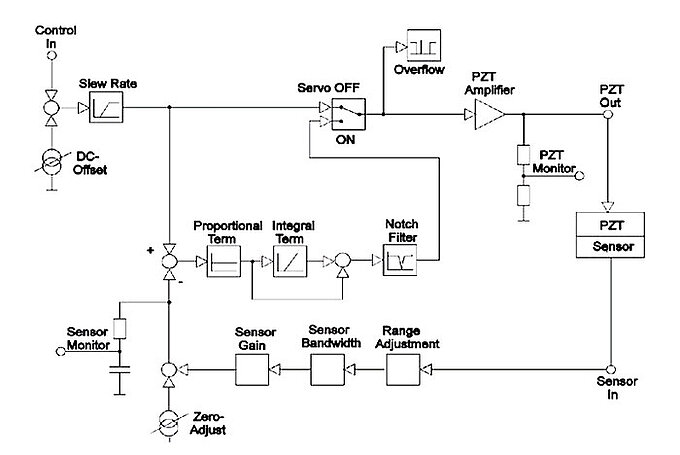
In addition to the sensor type, the controller concept also has a strong influence on performance parameters, such as settling, linearity, and bandwidth. Two basic controller types are commonly used with piezo nanopositioning systems: classical, analog servos (can have a digital command interface) and digital servos (can also have analog command interface). Learn more on analog and digital servo controllers.

Comparison of Piezoresistive and Capacitive Dual Plate Sensors
| Piezoresistive Strain Gauge | Capacitive Dual Plate Sensor | |
| General | Low cost, high sensitivity | High stability / linearity, high sensitivity |
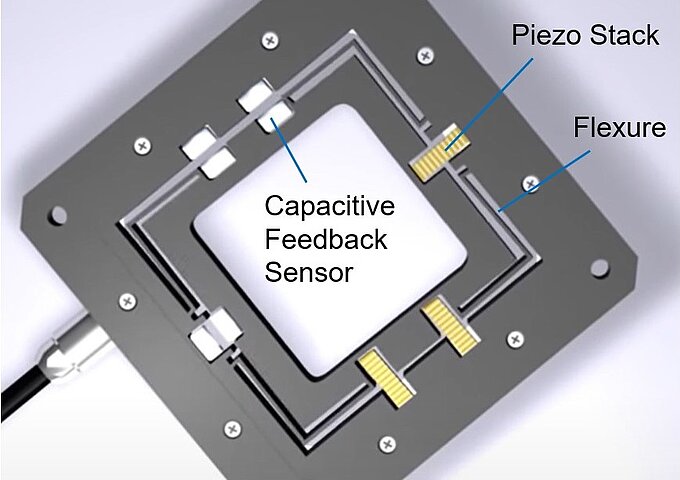
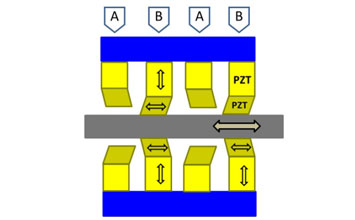
| Principle | PR sensor epoxy bonded to piezo element or part of a flexure. When the stage moves, the PR sensor sees strain causing a change in resistance. The change in resistance is interpreted as position change by the controller. | Capacitive sensors measure movement of the stage platform directly by sensing the gap between moving platform and the fixed frame. |
| Type of Measurement | Inferred measurement | Direct measurement |
| Best for | High resolution positioning / scanning with relative movement requirements | High resolution positioning / scanning where long term stability, absolute position, and repeatability are critical |
| Immunity to external electric noise | Fair (DC output signal) | Best (RF signal with high precision fixed-frequency reference) |
| Relative Cost | Low cost | About $1000 per axis higher than PR due to additional, higher precision mechanical and electronics components |
| Temp. sensitivity | Fair | Very low |
| Bandwidth | Very Good | Very Good |
| Parasitic errors | No compensation possible | Compensation possible |
| Long-term pos. stability | Fair. The sensor is bonded to a surface that is bent or stretched. Basically, the sensor floats on a thin film of epoxy. If stain is added, drift in the nanometer realm will occur. Piezoresistive sensors are semiconductors and temperature changes have a significant effect. | Nanoscale over 30min. There is no strain on the sensor and no contact. |
Stability Record
A new stability record with sub-nanometer drift was recently achieved by the National Institute of Standards (NIST). The published article describes a complex dual laser beam-based measurement system. The experiment setup employs an XYZ piezo stage with capacitive position sensors, model P561.3DD from PI.
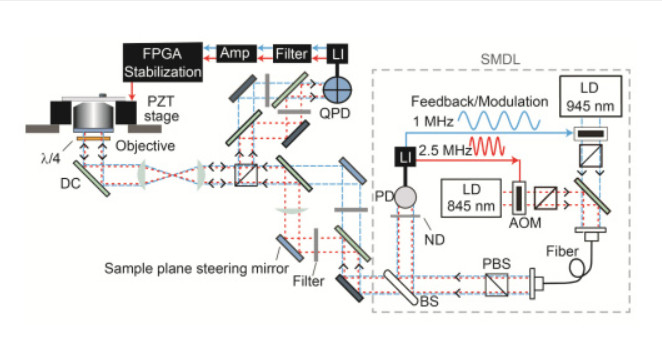

An applications article of the PInano P-545 XYZ stage (pictured left) in high resolution microscopy can be found is here:
“Continuous-Wave STED Microscope for Imaging Actin Cytoskeleton in Fixed and Live Cells”
Blog Categories
- Aero-Space
- Air Bearing Stages, Components, Systems
- Astronomy
- Automation, Nano-Automation
- Beamline Instrumentation
- Bio-Medical
- Hexapods
- Imaging & Microscopy
- Laser Machining, Processing
- Linear Actuators
- Linear Motor, Positioning System
- Metrology
- Microscopy
- Motorized Precision Positioners
- Multi-Axis Motion
- Nanopositioning
- Photonics
- Piezo Actuators, Motors
- Piezo Mechanics
- Piezo Transducers / Sensors
- Precision Machining
- Semicon
- Software Tools
- UHV Positioning Stage
- Voice Coil Linear Actuator
- X-Ray Spectroscopy